If, when trying this component out, you find that you have a particular use case that is not covered, or you have difficulty using this component, please reach out to the HDS team.
The Hds::Table component should be used for displaying tabular data; it renders an HTML table element.
This component takes advantage of the sort-by helper provided in ember-composable-helpers. While some of the examples provided on this page use some of the other helpers provided in this addon, they are not required to use the design system. Read the configuration information provided by the addon if you wish to customize which helpers are included in your own app.
The Table component itself is where most of options will be applied. Use of the component API (below) will automatically render sortable columns if desired.
Additionally, there are child components that can also be used to provide custom options.
- The
Hds::Table::Trcomponent is a template-only component. It supports...attributesbut is not eligible to receive interactions. It can containHds::Table::ThorHds::Table::Tdcomponents. - The
Hds::Table::Thcomponent is a template-only component. It supports...attributesbut is not eligible to receive interactions itself, although it can contain interactive elements. However, it is not likely that you will need to add interactive elements to this component as the sorting is already otherwise provided for. - The
Hds::Table::Tdcomponent is a template-only component. It supports...attributesbut is not eligible to receive interactions itself; however it can contain interactive elements.
- Name
-
<:head> - Type
-
named block - Description
-
This is a named block where the content for the table head (
<thead>) is rendered.
- Name
-
<:body> - Type
-
named block - Description
-
This is a named block where the content for the table body (
<tbody>) is rendered.
- Name
-
model - Type
-
array - Description
-
If defined, sets the data source that gets yielded by the
:bodynamed block.
- Name
-
columns - Type
-
array - Description
- If defined, sets the column header content and indicates that the table should be sorted. For more information about how this array is shaped, look at the code examples in the "How to Use" section.
- Name
-
sortingKeys - Type
-
array - Description
-
If defined, indicates which columns should be sortable (if only
columnsis defined, all columns will be sortable). For more information about how this array is shaped, look at the code examples in the "How to Use" section.
- Name
-
sortBy - Type
-
string - Description
- If defined, indicates which column should be pre-sorted when the table is rendered. For more information about how this value, look at the code examples in the "How to Use" section.
- Name
-
sortOrder - Type
-
string - Values
-
- asc (default)
- desc
- Description
-
Use in conjunction with
sortBy. If defined, indicates which direction the column should be pre-sorted in. All columns are unsorted by default.
- Name
-
isStriped - Type
-
boolean - Description
-
If set to
false, zebra striping on the table will not be applied.
- Name
-
density - Type
-
enum - Values
-
- short
- medium (default)
- tall
- Description
- If set, determines the density, or height, of the row.
- Name
-
valign - Type
-
enum - Values
-
- top (default)
- middle
- bottom
- baseline
- sub
- text-top
- Description
- If set, determines the vertical alignment of table's cell (td) content. While the acceptable values contain all of the values that the CSS property accepts, the default (top) and middle are the values most likely to be used.
- Name
-
caption - Type
-
string - Description
- Adds a (non-visible) caption for users with assistive technology. If set on a sortable table, the provided table caption is paired with the automatically generated sorted message text.
- Name
-
…attributes - Description
-
Supported for the
Hds::Tablecomponent.
There are several ways to implement the table component. These examples will be in order of increasing complexity. Additional implementation examples are in the Showcase section.
Static Table (non-sortable)
If you have your own content and don't want to use a model, you can still benefit from the components themselves. Here is an example of such an invocation in a template:
<!-- app/templates/components/table.hbs -->
<Hds::Table>
<:head as |H|>
<H.Tr>
<H.Th>Artist</H.Th>
<H.Th>Album</H.Th>
<H.Th>Release Year</H.Th>
</H.Tr>
</:head>
<:body as |B|>
<B.Tr>
<B.Td>Custom Cell Content</B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td>Some other custom cell content</B.Td>
</B.Tr>
</:body>
</Hds::Table>
Simple Table with model defined (non-sortable)
In this invocation of the table component, you would define the data model and insert your own content into the :head and :body blocks. Here is an example of such an invocation in a template:
<!-- app/templates/components/table.hbs -->
<Hds::Table @model=>
<:head as |H|>
<H.Tr>
<H.Th>Artist</H.Th>
<H.Th>Album</H.Th>
<H.Th>Release Year</H.Th>
</H.Tr>
</:head>
<:body as |B|>
<B.Tr>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
</B.Tr>
</:body>
</Hds::Table>
For documentation purposes, we imitated fetching data from an API and working with that as our data model.
import Route from '@ember/routing/route';
export default class ComponentsTableRoute extends Route {
async model() {
let response = await fetch('/api/folk.json');
let { data } = await response.json();
return data.map((model) => {
let { attributes } = model;
return { ...attributes };
});
}
}
Sortable Table
For the sortable table, the invocation and use is a little bit different:
1. Shape the data model for use; in this example we've placed it in the page's route. In this example, we're identifying the column headers (keys) and also capitalizing them. Each column object has two pieces: a key-- used for the model, the sortingKeys and sortBy; and the label-- used in the table header cells.
// app/routes/components/table.js
import Route from '@ember/routing/route';
import { capitalize } from '@ember/string';
export default class ComponentsTableRoute extends Route {
async model() {
let response = await fetch('/api/folk.json');
let { data } = await response.json();
// make sure the variable is declared outside of the loop
// so we can return it in the model response
let columns;
let dataResponse = data.map((model) => {
let { id, attributes } = model;
columns = Object.keys(attributes);
return { id, ...attributes };
});
columns = columns.map((column) => {
return { key: column, label: capitalize(column) };
});
return { data: dataResponse, columns };
}
}
2. Invoke the Hds::Table component in your template file.
<!-- app/templates/components/table.hbs -->
<Hds::Table
@model=
@columns=
>
<:body as |B|>
<B.Tr>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
</B.Tr>
</:body>
</Hds::Table>
If you want, you can indicate that only specific columns should be sortable.
<!-- app/templates/components/table.hbs -->
<Hds::Table
@model=
@columns=
@sortingKeys=
>
<:body as |B|>
<B.Tr>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
</B.Tr>
</:body>
</Hds::Table>
You can also indicate that a specific column should be pre-sorted.
<!-- app/templates/components/table.hbs -->
<Hds::Table
@model=
@columns=
@sortingKeys=
@sortBy='artist'
>
<:body as |B|>
<B.Tr>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
</B.Tr>
</:body>
</Hds::Table>
You can also indicate that a specific column should be pre-sorted in a specific direction.
<!-- app/templates/components/table.hbs -->
<Hds::Table
@model=
@columns=
@sortingKeys=
@sortBy='artist'
@sortOrder='desc'
>
<:body as |B|>
<B.Tr>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
</B.Tr>
</:body>
</Hds::Table>
Here's a table implementation that uses an array hash with localized strings for the column headers, indicates which columns should be sortable, and adds an overflow menu.
<!-- app/templates/components/table.hbs -->
<Hds::Table
@model=
@columns=
@sortingKeys=
>
<:body as |B|>
<B.Tr>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td></B.Td>
<B.Td>
<Hds::Dropdown as |dd|>
<dd.ToggleIcon
@icon='more-horizontal'
@text='Overflow Options'
@hasChevron=
@size='small'
/>
<dd.Interactive @route='components.table' @text='Create' />
<dd.Interactive @route='components.table' @text='Read' />
<dd.Interactive @route='components.table' @text='Update' />
<dd.Separator />
<dd.Interactive
@route='components.table'
@text='Delete'
@color='critical'
@icon='trash'
/>
</Hds::Dropdown>
</B.Td>
</B.Tr>
</:body>
</Hds::Table>
States of the sortable table header (buttons)
Static table with model defined
| Artist | Album | Release Year |
|---|---|---|
| Nick Drake | Pink Moon | 1972 |
| The Beatles | Abbey Road | 1969 |
| Melanie | Candles in the Rain | 1971 |
| Bob Dylan | Bringing It All Back Home | 1965 |
| James Taylor | Sweet Baby James | 1970 |
| Simon and Garfunkel | Bridge Over Troubled Waters | 1970 |
Static table with density set to "short"
| Artist | Album | Release Year |
|---|---|---|
| Nick Drake | Pink Moon | 1972 |
| The Beatles | Abbey Road | 1969 |
| Melanie | Candles in the Rain | 1971 |
| Bob Dylan | Bringing It All Back Home | 1965 |
| James Taylor | Sweet Baby James | 1970 |
| Simon and Garfunkel | Bridge Over Troubled Waters | 1970 |
Static table with density set to "tall"
| Artist | Album | Release Year |
|---|---|---|
| Nick Drake | Pink Moon | 1972 |
| The Beatles | Abbey Road | 1969 |
| Melanie | Candles in the Rain | 1971 |
| Bob Dylan | Bringing It All Back Home | 1965 |
| James Taylor | Sweet Baby James | 1970 |
| Simon and Garfunkel | Bridge Over Troubled Waters | 1970 |
Static table with no model defined
| Cell Header | Cell Header | Custom Width |
|---|---|---|
| Scope Row | Cell Content | Cell Content |
| Cell Content | Cell Content | Cell Content |
| Cell Content | Cell Content | Cell Content |
Static table with row striping
| Artist | Album | Release Year |
|---|---|---|
Sortable table (all columns sortable)
| Nick Drake | Pink Moon | 1972 |
| The Beatles | Abbey Road | 1969 |
| Melanie | Candles in the Rain | 1971 |
| Bob Dylan | Bringing It All Back Home | 1965 |
| James Taylor | Sweet Baby James | 1970 |
| Simon and Garfunkel | Bridge Over Troubled Waters | 1970 |
Sortable table (only some columns sortable)
| Release Year | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nick Drake | Pink Moon | 1972 |
| The Beatles | Abbey Road | 1969 |
| Melanie | Candles in the Rain | 1971 |
| Bob Dylan | Bringing It All Back Home | 1965 |
| James Taylor | Sweet Baby James | 1970 |
| Simon and Garfunkel | Bridge Over Troubled Waters | 1970 |
Sortable table, some columns sortable, artist column pre-sorted.
| Release Year | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bob Dylan | Bringing It All Back Home | 1965 |
| James Taylor | Sweet Baby James | 1970 |
| Melanie | Candles in the Rain | 1971 |
| Nick Drake | Pink Moon | 1972 |
| Simon and Garfunkel | Bridge Over Troubled Waters | 1970 |
| The Beatles | Abbey Road | 1969 |
Sortable table, last column not sortable and has custom width.
| Other | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nick Drake | Pink Moon | 1972 |
|
| The Beatles | Abbey Road | 1969 |
|
| Melanie | Candles in the Rain | 1971 |
|
| Bob Dylan | Bringing It All Back Home | 1965 |
|
| James Taylor | Sweet Baby James | 1970 |
|
| Simon and Garfunkel | Bridge Over Troubled Waters | 1970 |
|
Table where last column has right-aligned text
| Vinyl Cost (USD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nick Drake | Pink Moon | 1972 | 29.27 |
| The Beatles | Abbey Road | 1969 | 25.99 |
| Melanie | Candles in the Rain | 1971 | 46.49 |
| Bob Dylan | Bringing It All Back Home | 1965 | 229.00 |
| James Taylor | Sweet Baby James | 1970 | 16.00 |
| Simon and Garfunkel | Bridge Over Troubled Waters | 1970 | 20.49 |
Table with various cell content
| Additional Actions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nick Drake |
Pink Moon
|
1972
|
|
| The Beatles |
Abbey Road
|
1969
|
|
| Melanie |
Candles in the Rain
|
1971
|
|
| Bob Dylan |
Bringing It All Back Home
|
1965
|
|
| James Taylor |
Sweet Baby James
|
1970
|
|
| Simon and Garfunkel |
Bridge Over Troubled Waters
|
1970
|
Table with multi-line content
| Artist | Album | Quote |
|---|---|---|
| Nick Drake | Pink Moon | “The song is very special. It's an old song by a guy named Nick Drake. It's called 'Pink Moon' and is actually a very good introduction to Nick Drake if you're not familiar with him. It's very transporting. And to us seemed very fitting for a beautiful drive in the country on a very special night.” |
| The Beatles | Abbey Road | “it was the Beatles' last love letter to the world...lush, rich, smooth, epic, emotional and utterly gorgeous” |
| Melanie | Candles in the Rain | “Candles in the Rain matched material and interpretation with greater skill than she had in the past, and it ranks with her finest work” |
| Bob Dylan | Bringing It All Back Home | “By fusing the Chuck Berry beat of the Rolling Stones and the Beatles with the leftist, folk tradition of the folk revival, Dylan really had brought it back home, creating a new kind of rock & roll that made every type of artistic tradition available to rock.” |
| James Taylor | Sweet Baby James | “(It) struck a chord with music fans, especially because of its attractive mixture of folk, country, gospel, and blues elements, all of them carefully understated and distanced.” |
| Simon and Garfunkel | Bridge Over Troubled Waters | “Perhaps the most delicately textured album to close out the 1960s from any major rock act.” |
Header Column
When to use
- To display and organize tabular data.
- When comparing, sorting, and filtering multi-dimensional data and objects.
When not to use
- As a layout mechanism.
- As a replacement for a spreadsheet or similar application.
Anatomy
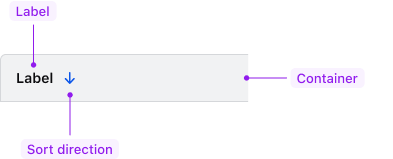
Label
Required
Sort direction
Options: none, indeterminate, ascending, descending
Column placement
| Start | Middle | End |
|---|
| Start | End |
|---|
| Full name | Projects | Email address | Status | Created by | Options |
|---|
This component has been designed and implemented with accessibility in mind. When used as recommended, there should not be any WCAG conformance issues with this component. Developers should ensure that any table customizations they implement also meet the applicable WCAG Success Criteria.
There are a few critical items for developers to note:
- The table row element (
tr) is not eligible to receive interactions. If an interactive element is desired, place it within a table cell element (td). - When providing additional or alternative styles to the table element, do not change the
displayproperty in the CSS. This alters how the table is presented to the user with assistive technology, and they will no longer be presented with a table.
Applicable WCAG Success Criteria (Reference)
This section is for reference only. This component intends to conform to the following WCAG success criteria:
-
1.3.1
Info and Relationships (Level A):
Information, structure, and relationships conveyed through presentation can be programmatically determined or are available in text. -
1.3.2
Meaningful Sequence (Level A):
When the sequence in which content is presented affects its meaning, a correct reading sequence can be programmatically determined. -
1.4.1
Use of Color (Level A):
Color is not used as the only visual means of conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response, or distinguishing a visual element. -
1.4.10
Reflow (Level AA):
Content can be presented without loss of information or functionality, and without requiring scrolling in two dimensions. -
1.4.11
Non-text Contrast (Level AA):
The visual presentation of the following have a contrast ratio of at least 3:1 against adjacent color(s): user interface components; graphical objects. -
1.4.12
Text Spacing (Level AA):
No loss of content or functionality occurs by setting all of the following and by changing no other style property: line height set to 1.5; spacing following paragraphs set to at least 2x the font size; letter-spacing set at least 0.12x of the font size, word spacing set to at least 0.16 times the font size. -
1.4.13
Content on Hover or Focus (Level AA):
Where receiving and then removing pointer hover or keyboard focus triggers additional content to become visible and then hidden, the following are true: dismissible, hoverable, persistent (see link). -
1.4.3
Minimum Contrast (Level AA):
The visual presentation of text and images of text has a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 -
1.4.4
Resize Text (Level AA):
Except for captions and images of text, text can be resized without assistive technology up to 200 percent without loss of content or functionality. -
2.1.1
Keyboard (Level A):
All functionality of the content is operable through a keyboard interface. -
2.1.2
No Keyboard Trap (Level A):
If keyboard focus can be moved to a component of the page using a keyboard interface, then focus can be moved away from that component using only a keyboard interface. -
2.1.4
Character Key Shortcuts (Level A):
If a keyboard shortcut is implemented in content using only letter (including upper- and lower-case letters), punctuation, number, or symbol characters, then it should be able to be turned off, remapped, or active only on focus. -
2.4.3
Focus Order (Level A):
If a Web page can be navigated sequentially and the navigation sequences affect meaning or operation, focusable components receive focus in an order that preserves meaning and operability. -
2.4.7
Focus Visible (Level AA):
Any keyboard operable user interface has a mode of operation where the keyboard focus indicator is visible. -
4.1.1
Parsing (Level A):
In content implemented using markup languages, elements have complete start and end tags, elements are nested according to their specifications, elements do not contain duplicate attributes, and any IDs are unique. -
4.1.2
Name, Role, Value (Level A):
For all user interface components, the name and role can be programmatically determined; states, properties, and values that can be set by the user can be programmatically set; and notification of changes to these items is available to user agents, including assistive technologies.